A Model Context Protocol server that provides knowledge graph management capabilities. This server enables LLMs to create, read, update, and delete entities and relations in a persistent knowledge graph, helping AI assistants maintain memory across conversations. This is a Swift implementation of the official TypeScript Memory MCP Server.
Note: This Swift version requires macOS 14.0 or later. For broader platform support (including Windows, Linux, and macOS 11.0+), check out the Go language implementation: memory-mcp-server-go.
- Knowledge Graph Storage: Maintain a persistent graph of entities and their relationships
- Entity Management: Create, retrieve, update, and delete entities with custom types
- Relation Tracking: Define and manage relationships between entities in active voice
- Observation System: Add and remove observations about entities over time
- Powerful Search: Find relevant nodes by name, type, or observation content
- Persistent Storage: Data persists between sessions in a simple JSON format
-
create_entities- Create multiple new entities in the knowledge graphentities(array, required): Array of entity objects to createname(string): The name of the entityentityType(string): The type of the entityobservations(array of strings): Observations associated with the entity
-
create_relations- Create multiple new relations between entitiesrelations(array, required): Array of relation objectsfrom(string): The name of the entity where the relation startsto(string): The name of the entity where the relation endsrelationType(string): The type of the relation (in active voice)
-
add_observations- Add new observations to existing entitiesobservations(array, required): Array of observation additionsentityName(string): The name of the entity to add observations tocontents(array of strings): The observations to add
-
delete_entities- Delete multiple entities and their associated relationsentityNames(array, required): Array of entity names to delete
-
delete_observations- Delete specific observations from entitiesdeletions(array, required): Array of observation deletionsentityName(string): The name of the entity containing the observationsobservations(array of strings): The observations to delete
-
delete_relations- Delete multiple relations from the knowledge graphrelations(array, required): Array of relation objects to deletefrom(string): The source entity nameto(string): The target entity namerelationType(string): The relation type
-
read_graph- Read the entire knowledge graph- No parameters required
-
search_nodes- Search for nodes in the knowledge graph based on a queryquery(string, required): Search query to match against entity names, types, and observations
-
open_nodes- Open specific nodes in the knowledge graph by their namesnames(array, required): Array of entity names to retrieve
The easiest way to install is with the one-line installer, which automatically downloads the latest version and installs it to ~/.local/bin in your home directory:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/okooo5km/memory-mcp-server/main/install.sh | bashThe installer will:
- Create
~/.local/binif it doesn't exist - Add this directory to your PATH (in .zshrc or .bashrc)
- Download and install the latest version
- Make the binary executable
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/okooo5km/memory-mcp-server.git cd memory-mcp-server -
Build the project:
swift build -c release
-
Install the binary:
# Install to user directory (recommended, no sudo required) mkdir -p ~/.local/bin cp $(swift build -c release --show-bin-path)/memory-mcp-server ~/.local/bin/
Make sure
~/.local/binis in your PATH by adding to your shell configuration file:echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.zshrc # or ~/.bashrc source ~/.zshrc # or source ~/.bashrc
The server supports the following command line arguments:
-h, --help: Display help information about the server, its usage, and available options-v, --version: Display the version number of the memory-mcp-server
Example usage:
# Display help information
memory-mcp-server --help
# Display version information
memory-mcp-server --versionThe server supports the following environment variables:
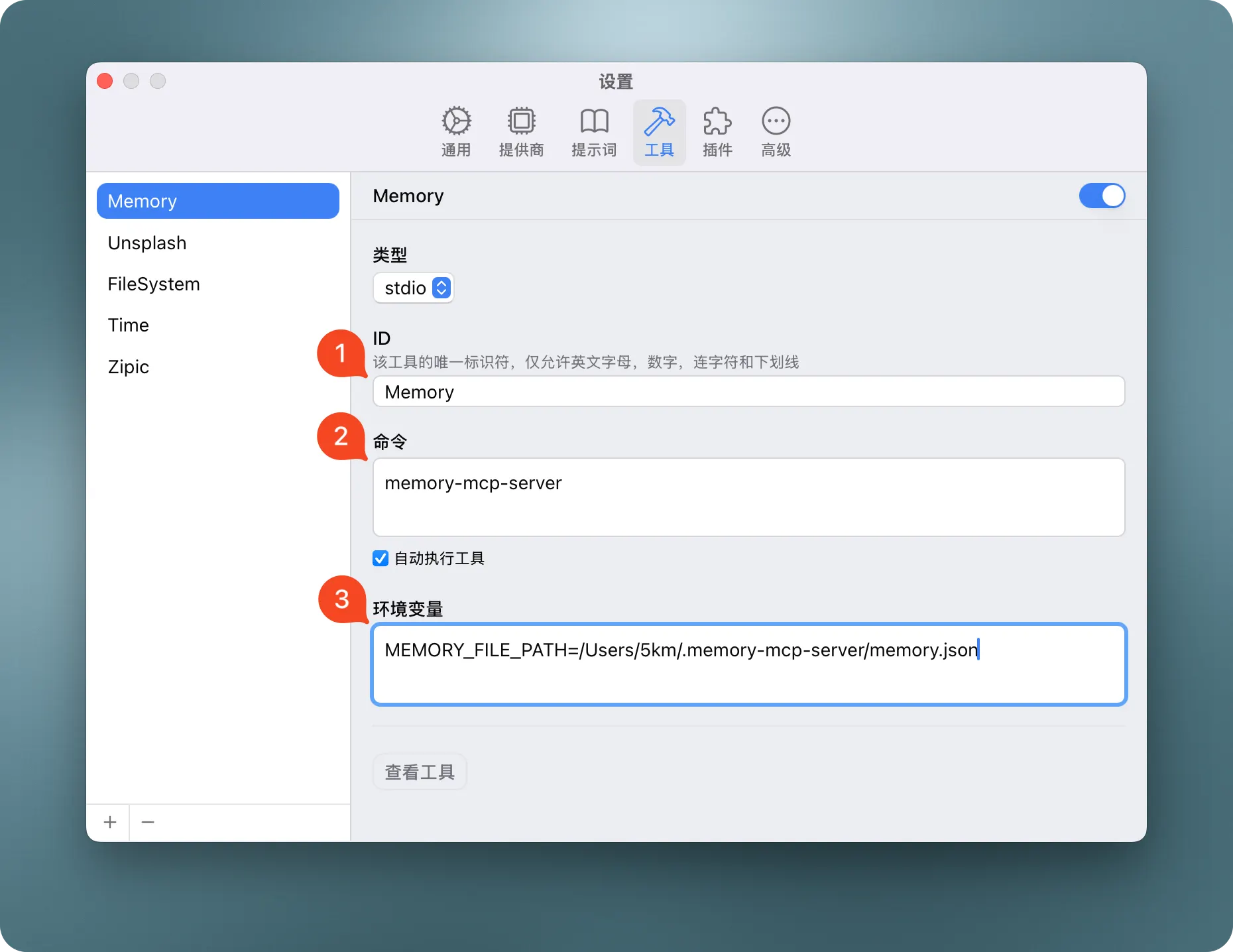
MEMORY_FILE_PATH: Custom path for storing the knowledge graph (optional)- If not specified, defaults to
memory.jsonin the current working directory - Can be an absolute path or relative to the current working directory
- If not specified, defaults to
You can check the configured file path in the server logs when starting the server.
export MEMORY_FILE_PATH="/path/to/your/memory.json"Add to your Claude settings:
"mcpServers": {
"memory": {
"command": "memory-mcp-server",
"env": {
"MEMORY_FILE_PATH": "/path/to/your/memory.json"
}
}
}Add the following configuration to your Cursor editor's Settings - mcp.json:
{
"mcpServers": {
"memory": {
"command": "memory-mcp-server",
"env": {
"MEMORY_FILE_PATH": "/path/to/your/memory.json"
}
}
}
}Add the memory MCP server to your Chatwise Settings - Tools.
You can use the following system prompt to help Claude utilize the memory-mcp-server effectively:
You have access to a Knowledge Graph memory system, which can store and retrieve information across conversations. Use it to remember important details about the user, their preferences, and any facts they've shared.
When you discover important information, save it using memory tools:
- `create_entities` to add new people, places, or concepts
- `create_relations` to record how entities relate to each other
- `add_observations` to record facts about existing entities
Before answering questions that might require past context, check your memory:
- `search_nodes` to find relevant information
- `open_nodes` to retrieve specific entities
- `read_graph` to get a complete view of your knowledge
Always prioritize information from your memory when responding to the user, especially when they reference past conversations.
- Swift 6.0 or later
- macOS 14.0 or later
- MCP Swift SDK 0.2.0 or later
The Memory MCP Server uses a simple graph structure to store knowledge:
- Entities: Nodes in the graph with a name, type, and list of observations
- Relations: Edges between entities with a relation type in active voice
- Observations: Facts or details associated with entities
The knowledge graph is persisted to disk as a line-delimited JSON file, where each line is either an entity or relation object.
{
"entities": [
{
"name": "John Smith",
"entityType": "Person",
"observations": ["Software engineer", "Lives in San Francisco", "Enjoys hiking"]
},
{
"name": "Acme Corp",
"entityType": "Company",
"observations": ["Founded in 2010", "Tech startup"]
}
]
}{
"relations": [
{
"from": "John Smith",
"to": "Acme Corp",
"relationType": "works at"
}
]
}{
"observations": [
{
"entityName": "John Smith",
"contents": ["Recently promoted to Senior Engineer", "Working on AI projects"]
}
]
}{
"query": "San Francisco"
}{
"names": ["John Smith", "Acme Corp"]
}- Long-term Memory for AI Assistants: Enable AI assistants to remember user preferences, past interactions, and important facts
- Knowledge Management: Organize information about people, places, events, and concepts
- Relationship Tracking: Maintain networks of relationships between entities
- Context Persistence: Preserve important context across multiple sessions
- Journal and Daily Logs: Maintain a structured record of events, activities, and reflections over time, making it easy to retrieve and relate past experiences chronologically
See GitHub Releases for version history and changelog.
If you find Memory MCP Server helpful, please consider supporting its development:
- ⭐️ Star the project on GitHub
- 🐛 Report bugs or suggest features
- 💝 Support via:

memory-mcp-server is licensed under the MIT License. This means you are free to use, modify, and distribute the software, subject to the terms and conditions of the MIT License.
A Swift implementation of a knowledge graph memory server for Model Context Protocol (MCP), enabling persistent memory capabilities for large language models. This project is based on the official TypeScript implementation but rewritten in Swift using the MCP Swift SDK.